CodingTEST
[백준 1325] 효율적인 해킹 (JAVA)
경걍
2023. 8. 23. 22:57
반응형
백준 1325번 문제 - 효율적인 해킹
1325번: 효율적인 해킹
첫째 줄에, N과 M이 들어온다. N은 10,000보다 작거나 같은 자연수, M은 100,000보다 작거나 같은 자연수이다. 둘째 줄부터 M개의 줄에 신뢰하는 관계가 A B와 같은 형식으로 들어오며, "A가 B를 신뢰한
www.acmicpc.net
문제 분석

- 하나의 컴퓨터만 해킹했을 때, 가장 많은 컴퓨터를 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 번호 모두 출력 (오름차순)
- A B 입력 됬을 때, B를 해킹하면 A도 해킹 가능
- ex. 1 → 3 → 4, 5 | 2 → 3 → 4, 5
해결 키 포인트
- BFS(너비 우선 탐색) 개념 파악
- DFS 사용하면 시간초과 발생 (왜인지는 이유를 모른다)
- B를 해킹하면 A도 해킹하는 것이므로, lists[B].add(A)를 하는 거라 생각! 하지만, 이렇게 하면 시간초과나, 문제 틀림 발생!
그래서 lists[A].add(B)로 해서 나중에 BFS 할 때,
lists[index]의 인접리스트들(lists[index].get(j)에서 얻어진 값을 가지고 해킹 가능 컴퓨터 개수를 알아낸다.
너비 우선 탐색(BFS)
그래프 완전 탐색 기번 중 하나로, 그래프의 시작 노드에서 출발해 시작 노드를 기준으로 가까운 노드를 먼저 방문하면서 탐색하는 알고리즘이다.
너비 우선 탐색의 핵심 이론
- 한번 방문한 노드를 다시 방문하면 안되므로 노드 방문 여부를 체크할 배열이 필요
- 그래프는 인접 리스트로 표현
- DFS의 탐색 방식은 선입 선출 특성을 가짐 ( 큐 사용 )
알고리즘
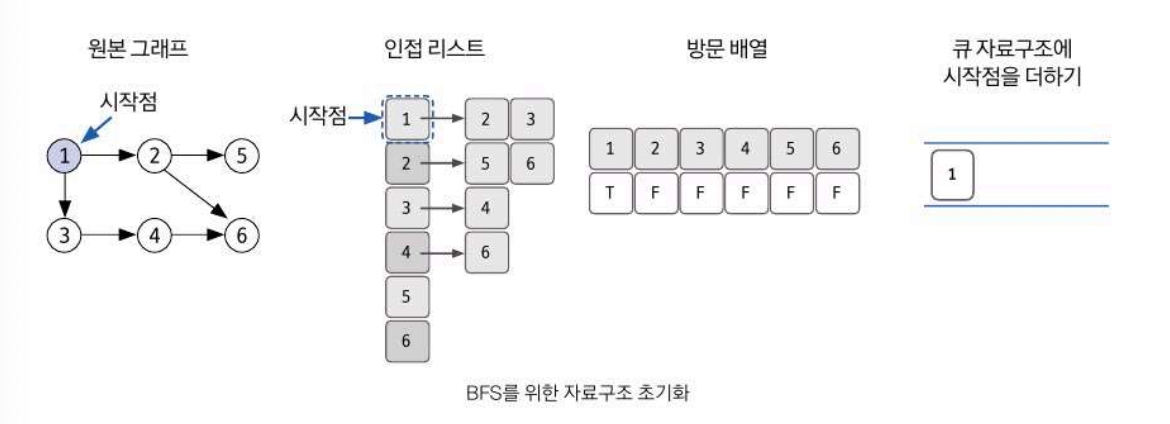
1. BFS를 시작할 노드를 정한 후 사용할 자료구조 초기화
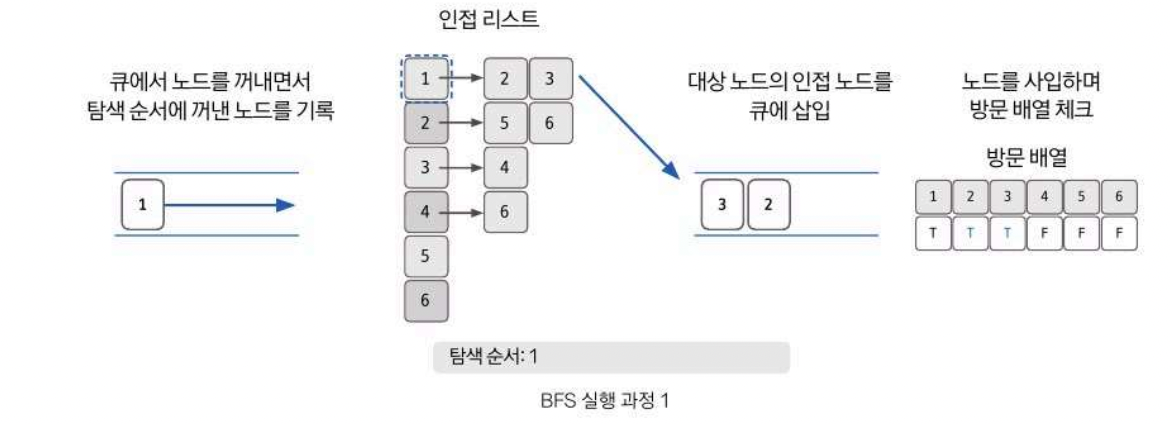
2. 큐에서 노드를 꺼낸 후 꺼낸 노드의 인접 노드를 다시 큐에 삽입 (이를 모든 정점에 다한다)
만약 큐에 노드가 없으면, 방문하지 않은 정점을 알아내, 큐에 삽입하고 다시 2번 단계를 반복한다.
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static ArrayList<Integer> [] lists;
static boolean [] isChecked;
static int [] counts;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
// N,M 입력
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 배열 초기화
isChecked = new boolean[N];
counts = new int[N];
lists = new ArrayList[N];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
lists[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// M개의 컴퓨터 관계 입력
for(int i=0;i<M;i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lists[a-1].add(b-1);
}
// i를 해킹 했을 때, 해킹 가능한 컴퓨터 수 알아내기
int max = 0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
isChecked = new boolean[N];
bfs(i);
}
// 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 개수의 최댓값 알아내기
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
max = Math.max(max, counts[i]);
}
// 가장 많이 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 개수가 max 인 것들의 index를 출력
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
if(counts[i] == max)
bw.write(i+1 + " ");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
public static void bfs(int index) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(index);
isChecked[index] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int now = queue.poll();
for(int i : lists[now]) {
if(isChecked[i] == false) {
isChecked[i] = true;
counts[i]++;
queue.add(i);
}
}
}
}
}DFS를 사용하고, list[b].add(a)를 사용해서 시간초과 된 예
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static ArrayList<Integer> [] lists;
static boolean [] isChecked;
static int [] counts;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
// N,M 입력
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 배열 초기화
isChecked = new boolean[N];
counts = new int[N];
lists = new ArrayList[N];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
lists[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// M개의 컴퓨터 관계 입력
for(int i=0;i<M;i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lists[b-1].add(a-1);
}
// i를 해킹 했을 때, 해킹 가능한 컴퓨터 수 알아내기
int max = 0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
isChecked = new boolean[N];
bfs(i, i);
}
// 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 개수의 최댓값 알아내기
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
max = Math.max(max, counts[i]);
}
// 가장 많이 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 개수가 max 인 것들의 index를 출력
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
if(counts[i] == max)
bw.write(i+1 + " ");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
public static void bfs(int index, int countIndex) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(index);
isChecked[index] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int now = queue.poll();
for(int i : lists[now]) {
if(isChecked[i] == false) {
isChecked[i] = true;
counts[countIndex]++;
queue.add(i);
}
}
}
}
}반응형